The idea of green banking has been introduced to enable banks to minimize their carbon footprint and to implement eco-friendly strategies such as modifying their lending principles and strategies to reduce industrial pollution. The green banking idea is a recent and least defined concept in Pakistan. Under Pakistan, Environmental Protection Act 1997 (State bank Pakistan, 2017), the first time the State Bank of Pakistan released green banking guidelines.
What is Green Banking?
Green Banking is an umbrella term for practices and guidance that urge banks to take responsibility for the environment, society, and the economy. The bank industry may also play a significant intermediary role in encouraging environmentally friendly and socially responsible investment between economic growth and environmental protection. In general, the banking sector is not viewed as a polluting industry but can have environmental consequences as energy use (lighting, air conditioning) and paper use rise. Banks and financial institutions can play a crucial part in global efforts to reduce and maintain environmental harm. The main aim of green banking is to minimize filthiness and to improve environmental and social impact. Banks have taken numerous steps, such as trade finance, digitalization, directing resources into sustainable projects, and CSR activities, to ensure that everybody can have convenient financial services. Banks play a vital part in enhancing government efforts at effective carbon emissions reduction to become socially Responsible Corporate Citizens (SRCC). In digitalization, many sectors have made huge strides, and the global banking sector is no exception. The banking sector is one of the largest consumers of resources such as paper and electricity through extensive branches and Automated Teller Machines (ATMs). Therefore, Green Banking can play an important role in reducing the negative environmental impact of a bank’s business operation through digital banking technology. Based on the customer’s real-time financial details, Banks can continue via cyberspace to stay in touch with its customers and provide unlimited services to reduce the use of different resources required to provide banking services through brick and mortar operations. This digitization of bank services would remove the industry’s carbon pollution and save money at the consumer end as well. Banks have introduced robots powered by Artificial Intelligence (AI) and Machine Learning to help clients search, transfer, and deposit money and seek advice on financial products. By using technology, banks can easily cut money laundering and use the consumer’s digital signature to complete the KYC process and protect the data using cryptographic techniques such as blockchain technologies.
Green Banking in Pakistan
The idea of green banking in Pakistan is quite new. The country is currently in the initial stages of the implementation of Green Banking. The first ‘digital policy of Pakistan’ was introduced in Pakistan in 2018. This strategy was mainly to support the IT sector through the development of a digital ecosystem. In December 2019, PM Imran Khan introduced a ‘New Pakistan Vision’ to increase connectivity, improve new infrastructures, increase investments in digital technologies, and encourage innovation and technology entrepreneurship. The swift introduction of crypto-currency is also a significant step in digitalizing and eventually greening the economic system. To reduce the possibility of money laundering, the Financial Action Task Force (FATF) has implemented cryptocurrency transactions guidelines. The Digital Pakistan Initiative is an endeavor by multiple organizations to take Pakistan to the era of industry 4.0 while the developing countries prepare and schedule their path towards IR 5.0. In a variety of businesses and governmental institutions in Pakistan, the effects of digitalization are emerging. Covid-19 has fueled demand for uplifting the e-commerce sector and steering digitization in Pakistan to enhance the IT sector and trade during the COVID-19. During the pandemic, a strict lockdown was implemented all over the country. During the lockdown restriction, online business demand boost-up rapidly. Faced with lockdown restrictions and store closures, consumers turn to online and mobile shopping to buy groceries, daily necessities, and other products. Ease of online shopping, payments made the feel people effective and becoming permanent practice for the majority, which will help succeed in the digital Pakistan campaign. The official also actively planning to promote online services to trade with other countries as well. The official stressed the development of cross-border e-commerce systems to promote trade and establish national e-commerce councils to promote start-ups, simplify payment options, reduce disputes, and protect consumer rights. Most banks began their mobile apps and web-based customer services. Digital systems are being introduced, such as digital wallets, One-Touch banking, biometric verification, cooperation with IT companies, and consumer data interconnection with other organizations. Pakistan State Bank (SBP) plans to launch digital currency by the year 2024. COVID-19 has intensively shaped our society over the last few months, and we are in the process of creating and adapting to the new norms. Changes have been observed while we live, shopping, studying, being entertaining, performing religious responsibilities, enjoying our festivals, and keeping in communication with our family. The digital tools were a lead in ensuring people’s safety and sustaining our economies through this pandemic. The Covid19 crisis could lead to a major change in digital lockdown payments. Major growth activity has recently been announced by Easypaisa, a popular Pakistani digital wallet. We reiterate our opinion that the strong potential for structural growth underpins Pakistan’s digital payment industry. Easypaisa confirmed a 35% rise in the number of new customers during the lockdown and estimated that inactive customers returned to service. When a lockdown was imposed, there’s been 17% increased daily transactions from the Easypaisa application. In the company, bank transactions via e.wallets have risen 184% overall, and smartphone uploads have increased by 15%. Covid-19 has massively increased e-commerce in Pakistan.
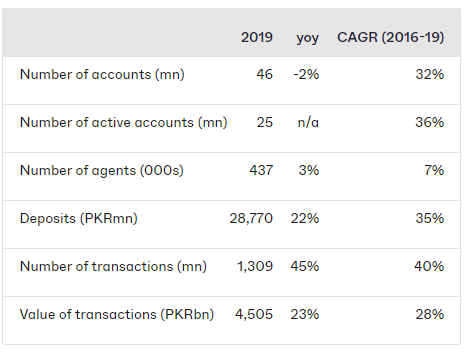
Pakistan mobile payments key statistics – 2019
Source: State Bank of Pakistan. Pakistan is a perfect place for stable digital banking. The country has a large unbanked population (79 percent of adults do not have a bank account), a high smartphone penetration (78 percent of the population have their mobile subscriptions), along with a high level of reliance on the currency. The overall number of accounts ranging from 46 million (34% of adults) to active accounts ranging in 25 million (18% of adults) has become low in mobile wallets. Growth for the number of accounts is low because all operators closed inactive accounts during the year on the central bank’s instruction. The impact of climate change on wildlife, agriculture, forestry, dry land, water supplies, and human health of global warming and climatic variations are now clear. Pakistan is sadly one of the most vulnerable countries to the consequences of climate change. As a developing country, Pakistan has significant social, political, economic, and environmental challenges, which need to be addressed for the country’s overall development. Digital banking or Green banking can answer many of our woes will allow our future generations to experience environmentally friendly business practices.